BRK – Brake
The brake (BRK) block provides access to the brake control unit of the Motor Interface for B-Box RCP. The Motor Interface for B-Box RCP features a brake…
The brake (BRK) block provides access to the brake control unit of the Motor Interface for B-Box RCP. The Motor Interface for B-Box RCP features a brake…
The torque sensor (TRQ) block reads the voltage output of a torque sensor and converts it to torque. It targets drive applications. The B-Box RCP…
The temperature sensor (TMP) block provides access to the temperature measurement from a PT100 or PT1000 sensor for drive applications. The B-Box RCP supports up…
The sin/cos encoder (S/C) block retrieves the Sine and Cosine signals of a sin/cos encoder connected to the Motor Interface. The B-Box RCP supports up…
The hall sensor interface (HAL) block provides access to the commutation signals from Hall effect sensors of a brushless DC motor. The B-Box RCP supports…
The resolver interface block decodes the feedback from a resolver and provides the position of the rotor for drive applications. The B-Box RCP supports up…
The incremental encoder interface (INC) block decodes the A, B, Z signals from an incremental encoder for motor drive applications. The B-Box supports up to…

What is the difference between Space Vector (SVPWM) and Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM)? This article presents the advantages of the SVPWM technique over SPWM…
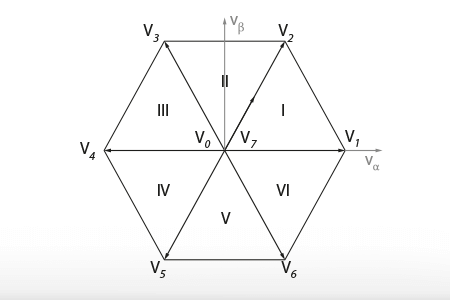
What is the space vector modulation technique (SVM) and how does it work? To answer these questions, this article introduces first the notions of active…
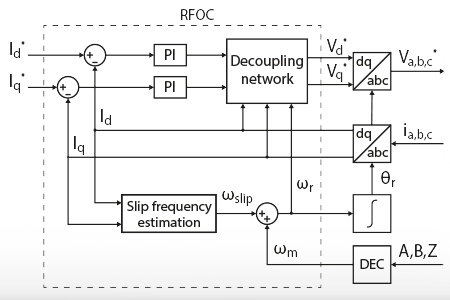
This note covers the rotor field-oriented control of an induction machine and its implementation on a user-configurable voltage-source inverter.
End of content
End of content